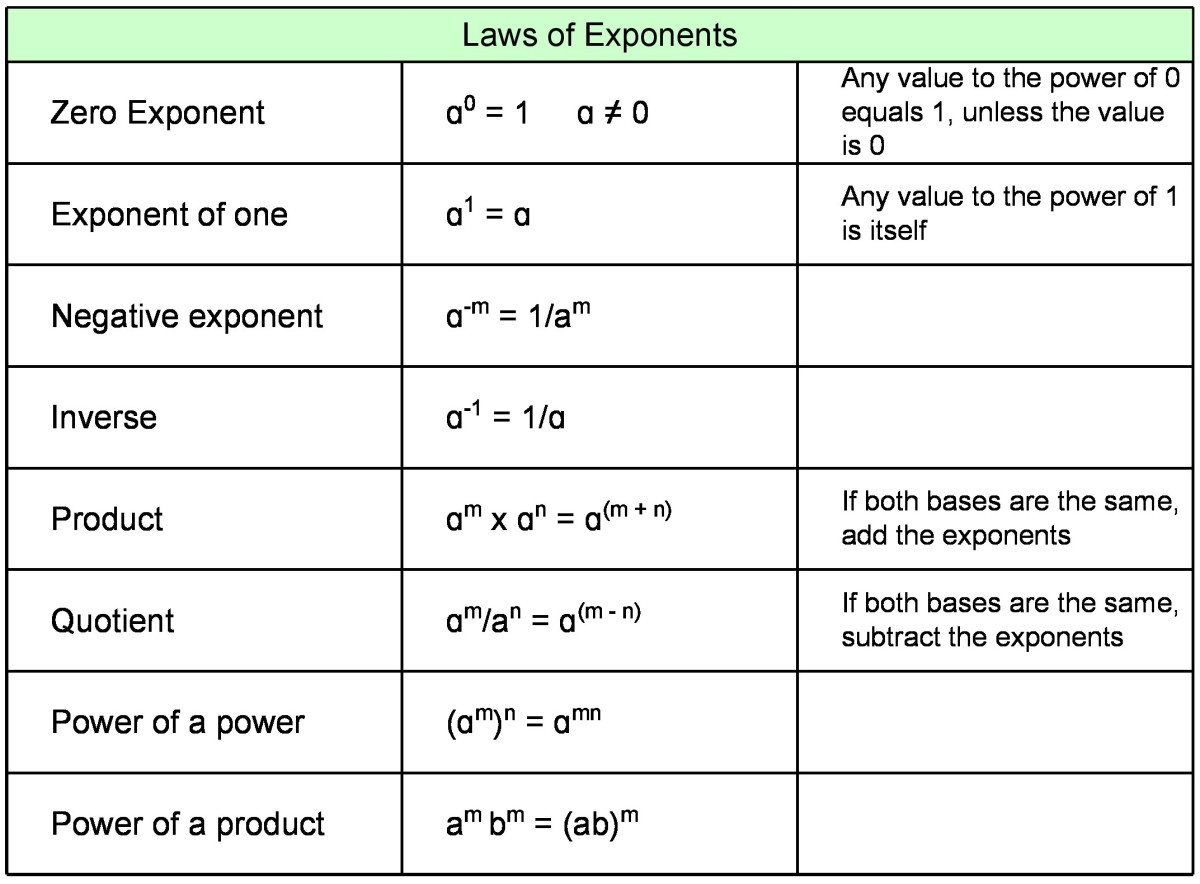
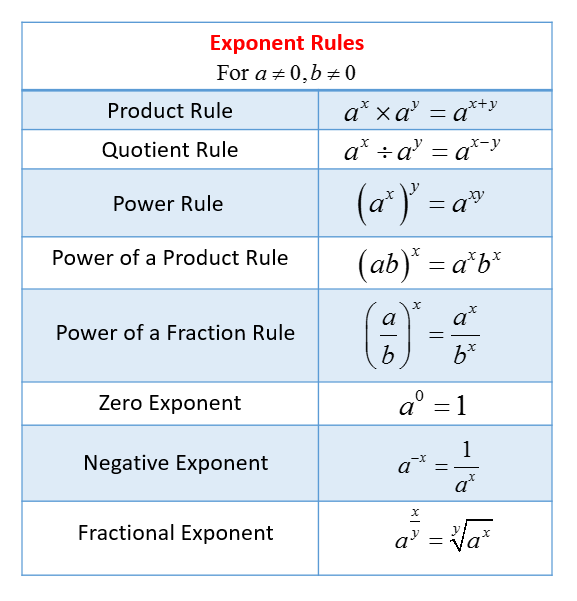
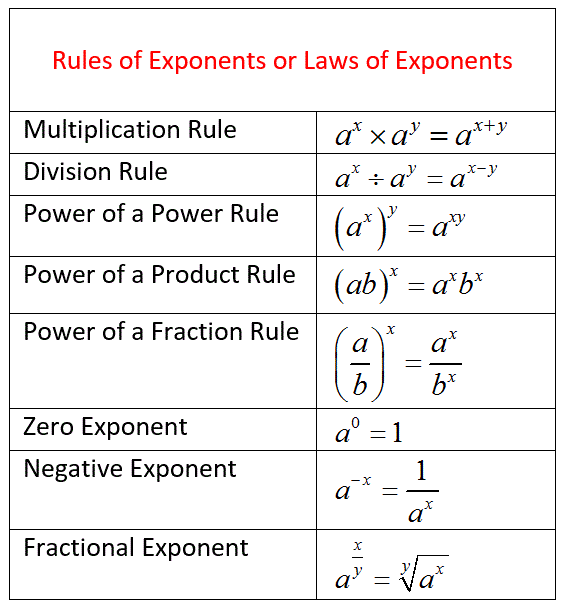
Rules Of Exponents Chart
Rules Of Exponents Chart - Web the rules of exponents allow you to simplify expressions involving exponents. Web learn how to use exponents and bases. When multiplying exponents with the same base, add the powers. When a base to an exponent is raised to another exponent, keep the base the same and multiply the exponents: A negative exponent tells you that the factor is on the wrong side of the fraction bar. Web rules of exponents 1. When x = 1, y = b: Learn about exponent rules, the zero rule of exponent, the negative rule of exponent, the product rule of exponent, and the quotient rule of exponent with the solved examples, and practice questions. Web properties of exponents. Web exponent rules are those laws that are used for simplifying expressions with exponents. \large\displaystyle \left (x^m\right)^n = x^ {mn} (xm)n = xmn. Web in this article, we are going to discuss the six important laws of exponents with many solved examples. The exponent laws are the tools needed for working with expressions involving exponents. A^n ⋅ a^m = a^ (n+m) illustration: When a base to an exponent is raised to another exponent, keep the base the same and multiply the exponents: Web properties of exponents. \large\displaystyle x^m \cdot x^n = x^ {m+n} xm ⋅ xn = xm+n. A n ⋅am = an m+ 3. 3 ) 2 = 2. Web rules, formulas and practice problems. Web properties of exponents. Web the rules of exponents allow you to simplify expressions involving exponents. ( x m n ) = x m × n the power rule. When multiplying exponents with the same base, add the powers. Web rules, formulas and practice problems. A negative exponent tells you that the factor is on the wrong side of the fraction bar. So for 5^2, you would use two 5's and multiply them together which is simply 5x5=25. A n am an m 3. Use the rules of exponents to simplify algebraic expressions. An am = an m− 4. The laws of exponents illustrate how to simplify numbers using the properties of. Web rules of exponents 1. Web the laws of exponents (also called rules of exponents) come from three ideas: Here we apply all the rules of exponents to simplify expressions. When x = 0, y = 1: So for 5^2, you would use two 5's and multiply them together which is simply 5x5=25. A n an − = 1 to move a number or a symbol from the numerator to the denominator (or from the denominator to the numerator), you must change the sign of the exponent. Web exponent rules are those laws that are used for. Multiplying exponents with the same power: For all real numbers x and y and real number constants m and n. ( x m n ) = x m × n the power rule. An am = an m− 4. Web the product rules for exponents. When bases are identical but exponents differ: Let's go over each rule in detail, and see some examples. X (1 n) = n√x. Power of a product rule: Web there are several laws of exponents (sometimes called exponent laws or rules of exponents), but this page will cover product rule, quotient rule, and negative exponent rule. A is the base and n is the exponent. When x = 1, y = b: Web rules, formulas and practice problems. ( x is not zero). Use the rules of exponents to simplify algebraic expressions. A 0 = 1 2. Multiplying exponents with the same base: When multiplying two quantities with the same base, add exponents: Web the laws of exponents (also called rules of exponents) come from three ideas: \large\displaystyle \left (x^m\right)^n = x^ {mn} (xm)n = xmn. 2^3 ⋅ 2^4 = 2^ (3+4) = 2^7 = 128. Web learn how to use exponents and bases. Web rules, formulas and practice problems. Web the exponent (the number 2) is the number of bases (the number 5) you multiply together. X ) a = b x* a. ( x m n ) = x m × n the power rule. Web there are several laws of exponents (sometimes called exponent laws or rules of exponents), but this page will cover product rule, quotient rule, and negative exponent rule. \large\displaystyle x^m \cdot x^n = x^ {m+n} xm ⋅ xn = xm+n. ( x is not zero). X (1. ( x m n ) = x m × n the power rule. ( x is not zero). When exponents are identical but bases differ: 3 ) 2 = 2. Exponential equations with fraction exponents. Web get started learning about the rules or laws of exponents with this comprehensive introduction. Web the rules of exponents allow you to simplify expressions involving exponents. Web rules, formulas and practice problems. A n an − = 1 to move a number or a symbol from the numerator to the denominator (or from the denominator to the numerator), you must change the sign of the exponent. Putting all the rules together, we can simplify more complex expression containing exponents. The base a raised to the power of n is equal to the multiplication of a, n times: A is the base and n is the exponent. Web the exponent (the number 2) is the number of bases (the number 5) you multiply together. A fractional exponent like 1/n means to take the nth root: A n = a × a ×. \large\displaystyle x^m \cdot x^n = x^ {m+n} xm ⋅ xn = xm+n.Exponent Rules Chart
Exponent Rules Laws of Exponents Exponent Rules Chart
Laws of Exponents and Indices with Examples [Video] Teachoo
Free Printable Exponent Rules Chart & Power Chart 110 [PDF
Rules of Logarithms and Exponents With Worked Examples and Problems
Exponents, Exponential Notation, and Scientific Notation (solutions
Rules Of Exponents Anchor Chart
Exponent Rules Law and Example Studying math, Learning mathematics
Rules Of Exponents Chart
Rules of Exponents (solutions, examples, songs, videos)
(A ) M N Amn 6.
When Dividing Two Quantities With The Same Base, Subtract Exponents:
Learn About Exponent Rules, The Zero Rule Of Exponent, The Negative Rule Of Exponent, The Product Rule Of Exponent, And The Quotient Rule Of Exponent With The Solved Examples, And Practice Questions.
Web The Product Rules For Exponents.
Related Post:


![Laws of Exponents and Indices with Examples [Video] Teachoo](https://d1avenlh0i1xmr.cloudfront.net/914d9e5c-9055-415c-8eb4-45ee41729114/exponent-law-with-examples.jpg)