Risk Of Chromosomal Abnormalities By Age Chart
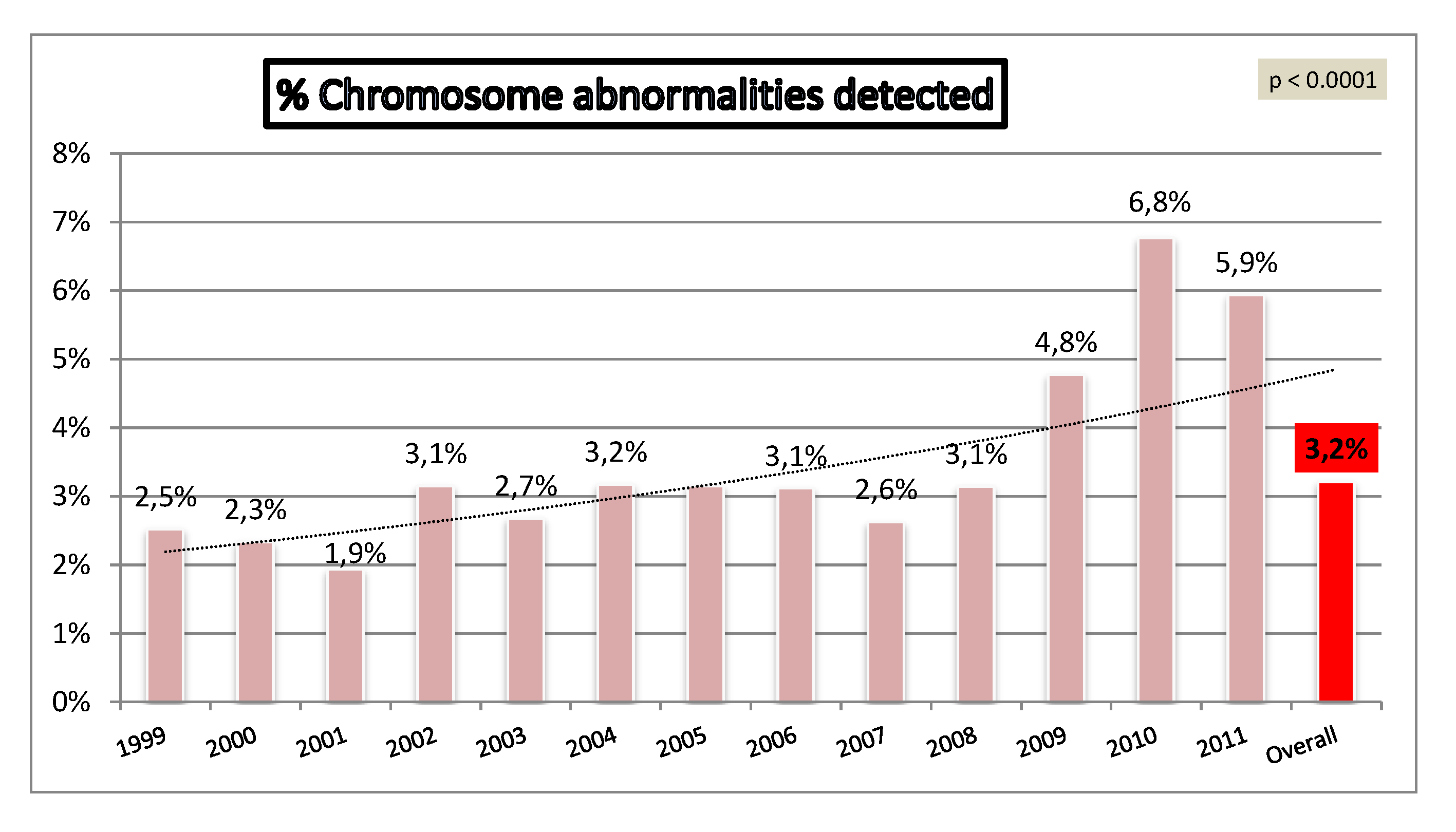
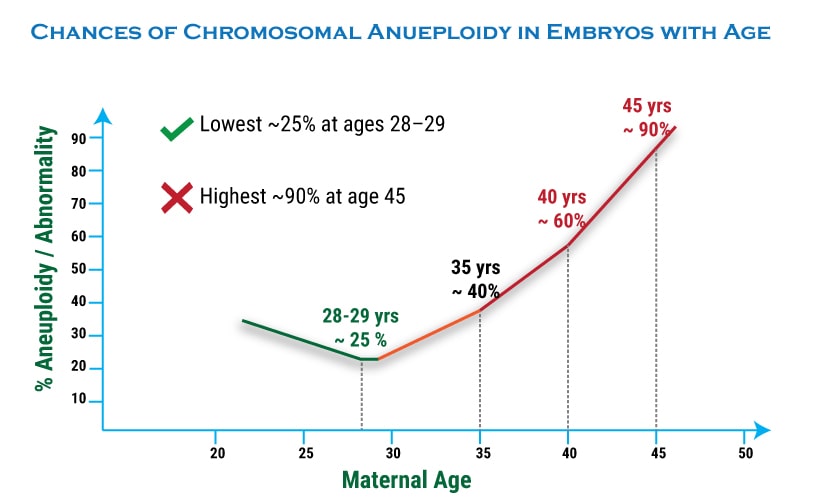
Risk Of Chromosomal Abnormalities By Age Chart - Web the risk of chromosomal abnormality increases with maternal age. Risks of having a baby with submicroscopic chromosomal. Enter the age of the mother at the time of delivery: Enter the age of the mother at the time of delivery: The calculator below calculates the theoretical risk for down syndrome and chromosome abnormalities in multiple gestations.*. The risk is about 1 in 1,250 for a woman. The table below shows the correlation of maternal age (mother's age) and the potential risk of human genetic abnormalities in children. The chance of having a child with down syndrome increases over time. Web home > calculators > risk for chromosome abnormalities at term. Web this practice bulletin has been revised to further clarify methods of screening for fetal chromosomal abnormalities, including expanded information regarding the use of cell. However, successful pregnancies are possible with. The chance of having a child with down syndrome increases over time. This is because errors in meiosis may be more likely to happen as a result. Web a retrospective cohort analysis using a large u.s. The risk is about 1 in 1,250 for a woman. Web the risk of fetal aneuploidy rises with increasing maternal age. Web home > calculators > risk for chromosome abnormalities at term. Data for table modified from hook et al from chromosomal abnormality. The chance of having a child affected by down syndrome increases from about 1 in 1,250 for a woman who. Aneuploid eggs and embryos are also. Trisomy 21 and trisomy 18 can happen at any age. Web this practice bulletin has been revised to further clarify methods of screening for fetal chromosomal abnormalities, including expanded information regarding the use of cell. Web the risk of fetal aneuploidy rises with increasing maternal age. Total risk for any chromosome abnormalities. Web risk of down’s syndrome and chromosomal abnormalities. The table below shows the correlation of maternal age (mother's age) and the potential risk of human genetic abnormalities in children. Risks of having a baby with submicroscopic chromosomal. Web the main cause of increased risk for miscarriage in “older” women is increased rates of chromosomal abnormalities in their eggs. The calculator below calculates the theoretical risk for down syndrome. Web chance of chromosome differences based on age. Web the incidence of aneuploidies increased exponentially with maternal age ( p <0.0001). Total risk for any chromosome abnormalities. Web a retrospective cohort analysis using a large u.s. Web the risk for chromosome problems increases with the mother's age. Web home > calculators > risk for chromosome abnormalities at term. Web the risk for chromosome problems increases with the mother's age. Web the overall risk of having a baby with a chromosome abnormality is small. The chance of having a child with down syndrome increases over time. Australian average maternal age change the first column shows maternal age, the. Web abnormality in multiple gestation*. Risks of having a baby with submicroscopic chromosomal. The calculator below calculates the theoretical risk for down syndrome and chromosome abnormalities in multiple gestations.*. Web home > calculators > risk for chromosome abnormalities at term. The risk is about 1 in 1,250 for a woman. Aneuploid eggs and embryos are also. Australian average maternal age change the first column shows maternal age, the second column shows the. Web this practice bulletin has been revised to further clarify methods of screening for fetal chromosomal abnormalities, including expanded information regarding the use of cell. Trisomy 21 and trisomy 18 can happen at any age. Total risk for. Web the incidence of aneuploidies increased exponentially with maternal age ( p <0.0001). The chance of having a child affected by down syndrome increases from about 1 in 1,250 for a woman who. Aneuploid eggs and embryos are also. Web chance of chromosome differences based on age. Web the main cause of increased risk for miscarriage in “older” women is. Web the estimated rate of all clinically significant cytogenetic abnormalities rises from about 2 per 1000 (1 per 500) at the youngest maternal ages to about 2.6 per 1000 (1 per 270) at. Trisomy 21 and trisomy 18 can happen at any age. Enter the age of the mother at the time of delivery: Web the overall risk of having. Web the incidence of aneuploidies increased exponentially with maternal age ( p <0.0001). But as you age, the risk of having a baby with missing, damaged, or extra chromosomes increases. However, successful pregnancies are possible with. Aneuploid eggs and embryos are also. Total risk for any chromosome abnormalities. Trisomy 21 and trisomy 18 can happen at any age. The chance increases as the pregnant individual gets older, as shown in the. In particular, the risk of trisomy 21 (standard error [se], 0.0378; Web risk of down’s syndrome and chromosomal abnormalities at live birth, according to maternal age. Enter the age of the mother at the time of delivery: Web advanced maternal age increases fertility challenges, risk of complications, and chromosomal abnormalities. Total risk for any chromosome abnormalities. Because fetal aneuploidy can affect any pregnancy, all pregnant women should be offered screening. Risks of having a baby with submicroscopic chromosomal. Enter the age of the mother at the time of delivery: Web the estimated rate of all clinically significant cytogenetic abnormalities rises from about 2 per 1000 (1 per 500) at the youngest maternal ages to about 2.6 per 1000 (1 per 270) at. Web the overall risk of having a baby with a chromosome abnormality is small. Web * this table includes only chromosomal abnormalities that can be detected by standard chromosomal testing. Web the incidence of aneuploidies increased exponentially with maternal age ( p <0.0001). In particular, the risk of trisomy 21 (standard error [se], 0.0378; Australian average maternal age change the first column shows maternal age, the second column shows the. The chance increases as the pregnant individual gets older, as shown in the. Web this practice bulletin has been revised to further clarify methods of screening for fetal chromosomal abnormalities, including expanded information regarding the use of cell. Web chance of chromosome differences based on age. Web abnormality in multiple gestation*. Web the risk of fetal aneuploidy rises with increasing maternal age.Table 1 from Maternal agespecific rates of fetal chromosomal
Risk Of Chromosomal Abnormalities By Maternal Age Chart
Risk Of Chromosomal Abnormalities By Age Chart
Risk Of Chromosomal Abnormalities By Maternal Age Chart
[PDF] Maternal agespecific rates of fetal chromosomal abnormalities in
Risk Of Chromosomal Abnormalities By Age Chart
Relationship between the incidence of clinically significant
Risk Of Chromosomal Abnormalities By Age Chart
Counseling Understanding Your DNA
The Chromosomal and Genomic Basis of Disease Thompson & Thompson
Web A Woman Age 35 Years Or Older Is At Higher Risk Of Having A Baby With A Chromosomal Abnormality.
Web The Main Cause Of Increased Risk For Miscarriage In “Older” Women Is Increased Rates Of Chromosomal Abnormalities In Their Eggs.
Trisomy 21 And Trisomy 18 Can Happen At Any Age.
The Risk Is About 1 In 1,250 For A Woman.
Related Post:



![[PDF] Maternal agespecific rates of fetal chromosomal abnormalities in](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/40dc865e8a4a02ff343d3419dff05fdf3c610199/4-Table2-1.png)