Domain And Kingdom Chart
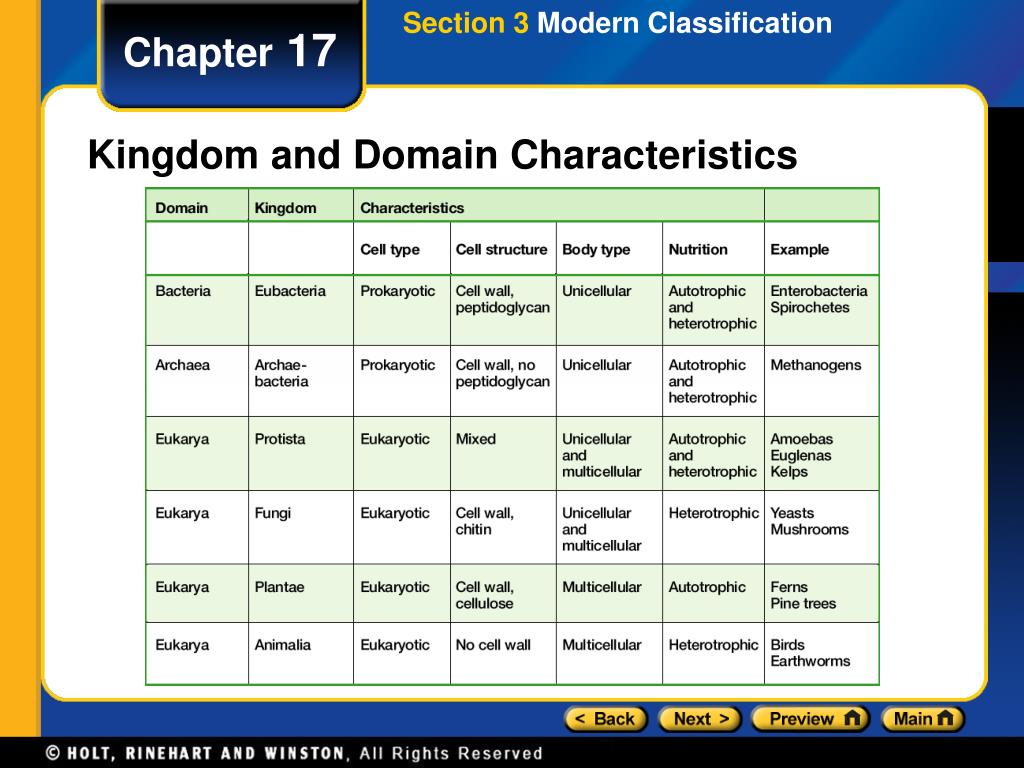
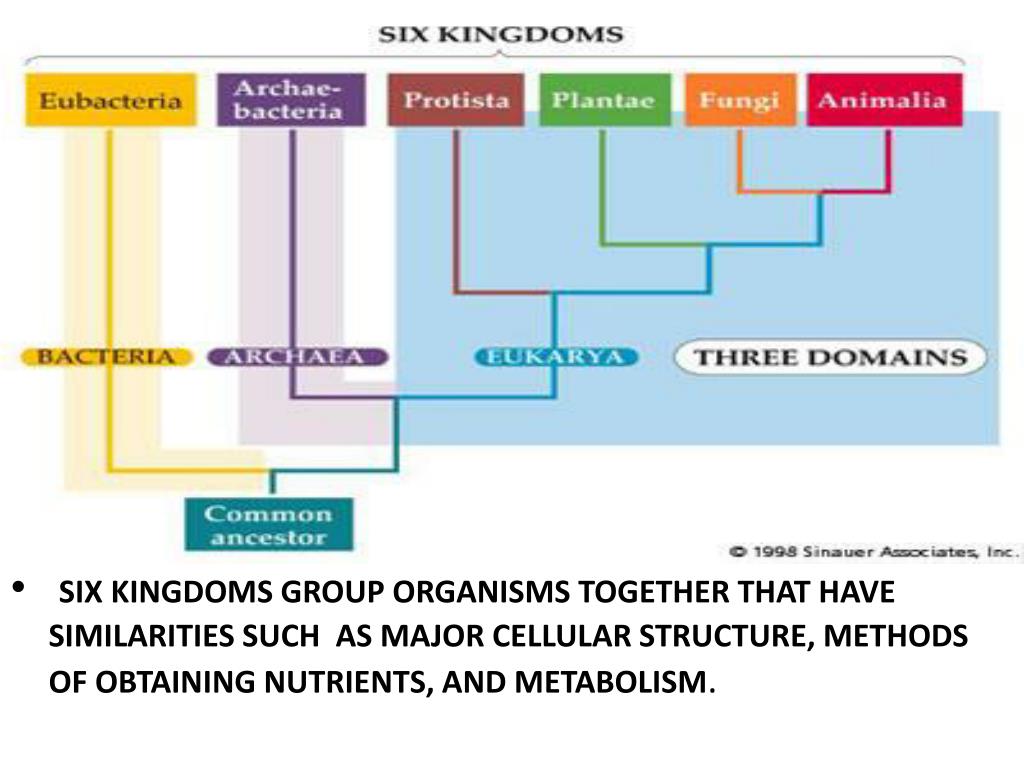
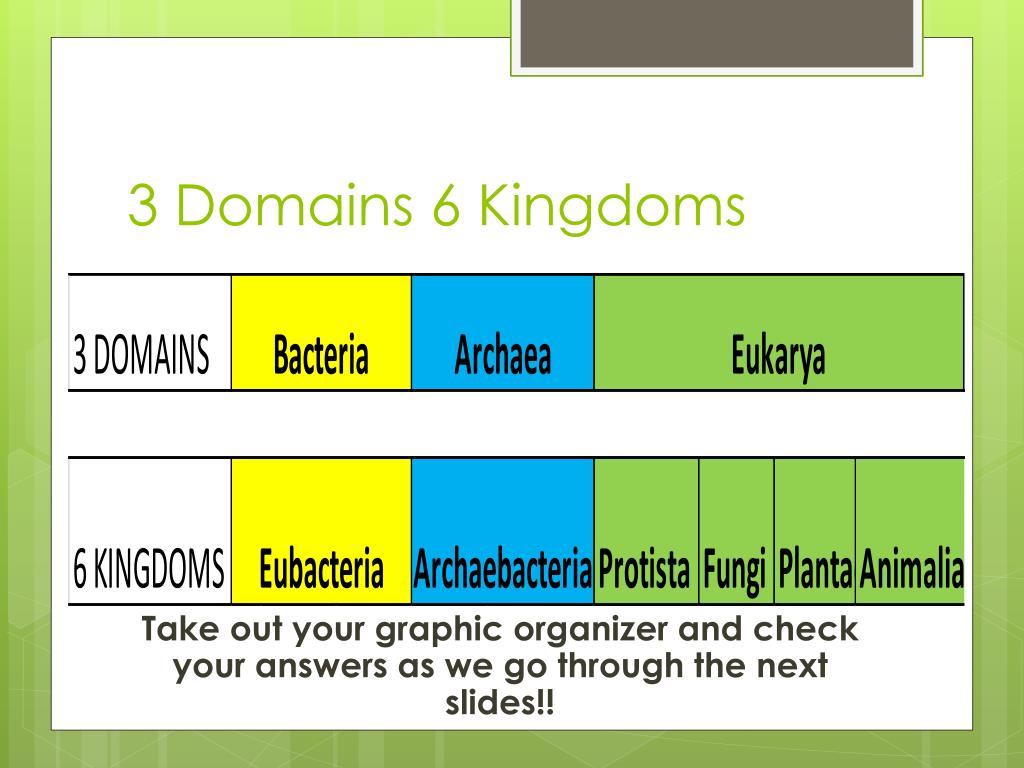
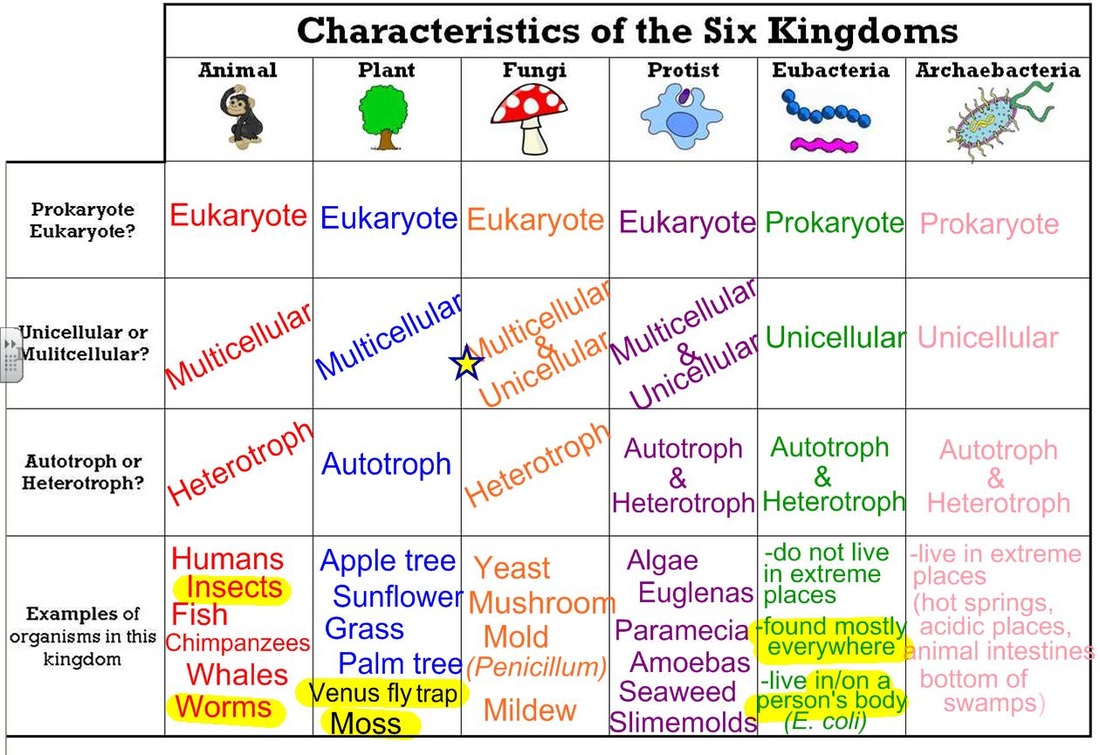
Domain And Kingdom Chart - Create a taxonomy, modeled on the linnaean classification system, for a set of common objects, such as motor vehicles, tools, or office supplies. In biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum. In other words, kingdoms are the second highest taxonomic rank. Web the 5 kingdoms of life are animalia, plantae, fungi, protista, and monera. Within each domain is a second category called a kingdom. The plant kingdom consists of 14. Web linnaeus invented binomial nomenclature, the system of giving each type of organism a genus and species name. He also developed a classification system called the taxonomic hierarchy, which today has eight ranks from general to specific: Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. Web within each of the three domains, we find kingdoms, the second category within taxonomic classification, followed by subsequent categories that include phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. Web carl linnaeus, the father of modern taxonomy, developed a system for classifying living organisms into categories like species, genus, order, class, and kingdom. Web linnaeus invented binomial nomenclature, the system of giving each type of organism a genus and species name. Web all organisms are traditionally classified into three domains and further subdivided into one of six kingdoms of life: Level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 1,200 mastery points! Within each domain is a second category called a kingdom. Web what is a domain? Identify the groupings that correspond to the different taxa in the linnaean system. Web the classification system commonly used today is based on the linnean system and has eight levels of taxa; From the most general to the most specific, these are domain, kingdom, phylum (plural, phyla), class, order, family, genus (plural, genera), and species. Phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species (figure 1). Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. Level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 1,200 mastery points! After kingdoms, the subsequent categories of increasing specificity are: Web the classification system commonly used today is based on the linnean system and has eight levels of taxa; Web for example, after the common beginning. Web carl linnaeus, the father of modern taxonomy, developed a system for classifying living organisms into categories like species, genus, order, class, and kingdom. Phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species (figure 1). From the most general to the most specific, these are domain, kingdom, phylum (plural, phyla), class, order, family, genus (plural, genera), and species. In other words, it. Archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia. From the most general to the most specific, these are domain, kingdom, phylum (plural, phyla), class, order, family, genus (plural, genera), and species. In other words, kingdoms are the second highest taxonomic rank. When there are 6 kingdoms, monera breaks into eubacteria and archaebacteria. Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics,. Web within each of the three domains, we find kingdoms, the second category within taxonomic classification, followed by subsequent categories that include phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. When there are 6 kingdoms, monera breaks into eubacteria and archaebacteria. Archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia. After kingdoms, the subsequent. After kingdoms, the subsequent categories of increasing specificity are: When there are 6 kingdoms, monera breaks into eubacteria and archaebacteria. Web linnaeus invented binomial nomenclature, the system of giving each type of organism a genus and species name. The fungus kingdom contains 8 phyla. Web each phylum is grouped into a kingdom, which is grouped into a domain. This tree of life helps us understand relationships between organisms. The fungus kingdom contains 8 phyla. Phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species (figure 1). Within each domain is a second category called a kingdom. The plant kingdom consists of 14. In other words, it is a broad classification of organisms according to their characteristics. Level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 1,200 mastery points! When there are 6 kingdoms, monera breaks into eubacteria and archaebacteria. Web all organisms are traditionally classified into three domains and further subdivided into one of six kingdoms of life:. Identify the groupings that correspond to the different taxa in the linnaean system. In biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum. When there are 6 kingdoms, monera breaks into eubacteria and archaebacteria. Create a taxonomy, modeled on the linnaean classification system, for a set of common objects, such as motor vehicles,. Identify the groupings that correspond to the different taxa in the linnaean system. Web for example, after the common beginning of all life, scientists divide organisms into three large categories called a domain: In other words, it is a broad classification of organisms according to their characteristics. The fungus kingdom contains 8 phyla. Phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. Web what is a domain? Web each phylum is grouped into a kingdom, which is grouped into a domain. Identify the groupings that correspond to the different taxa in the linnaean system. Web the 5 kingdoms of life are animalia, plantae, fungi, protista, and monera. Humans are part of the animal kingdom taxonomy. When there are 6 kingdoms, monera breaks into eubacteria and archaebacteria. Create a taxonomy, modeled on the linnaean classification system, for a set of common objects, such as motor vehicles, tools, or office supplies. Web linnaeus invented binomial nomenclature, the system of giving each type of organism a genus and species name. Web within each of the three domains, we find kingdoms, the second category within taxonomic classification, followed by subsequent categories that include phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. Within each domain is a second category called a kingdom. Identify the groupings that correspond to the different taxa in the linnaean system. The plant kingdom consists of 14. From the most general to the most specific, these are domain, kingdom, phylum (plural, phyla), class, order, family, genus (plural, genera), and species. Web the classification system commonly used today is based on the linnean system and has eight levels of taxa; Archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia. Level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 1,200 mastery points! Web all organisms are traditionally classified into three domains and further subdivided into one of six kingdoms of life: Humans are part of the animal kingdom taxonomy. After kingdoms, the subsequent categories of increasing specificity are: In other words, kingdoms are the second highest taxonomic rank. He also developed a classification system called the taxonomic hierarchy, which today has eight ranks from general to specific:An Introduction to Taxonomy The Kingdoms and Domains of Life
PPT Table of Contents PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1798916
PPT Classification Chapter 17 Taxonomy 6 Kingdoms Dissection notes
Domains Kingdoms Biology Eubacteria, Biology, Math
PPT Domains and Kingdoms PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
biological classification Students Britannica Kids Homework Help
️ Kingdom and domain characteristics. Mnemonic taxonomy / biology
Domain And Kingdom Chart
Classification « KaiserScience
Domains & Kingdoms 178 plays Quizizz
Web Each Phylum Is Grouped Into A Kingdom, Which Is Grouped Into A Domain.
The Animal Kingdom Contains Approximately 35 Phyla.
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, And Species.
The Fungus Kingdom Contains 8 Phyla.
Related Post: