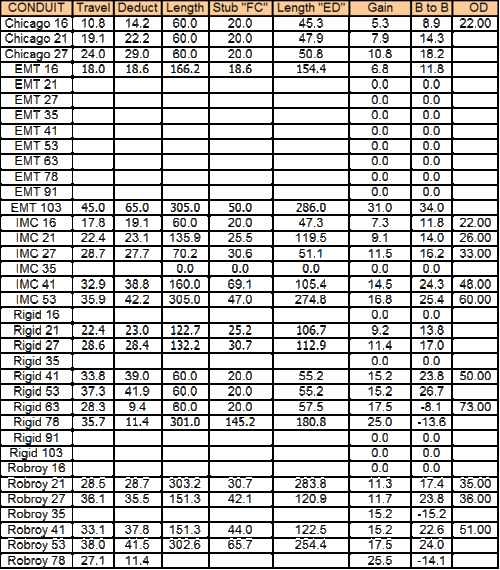
Conduit Shrinkage Chart
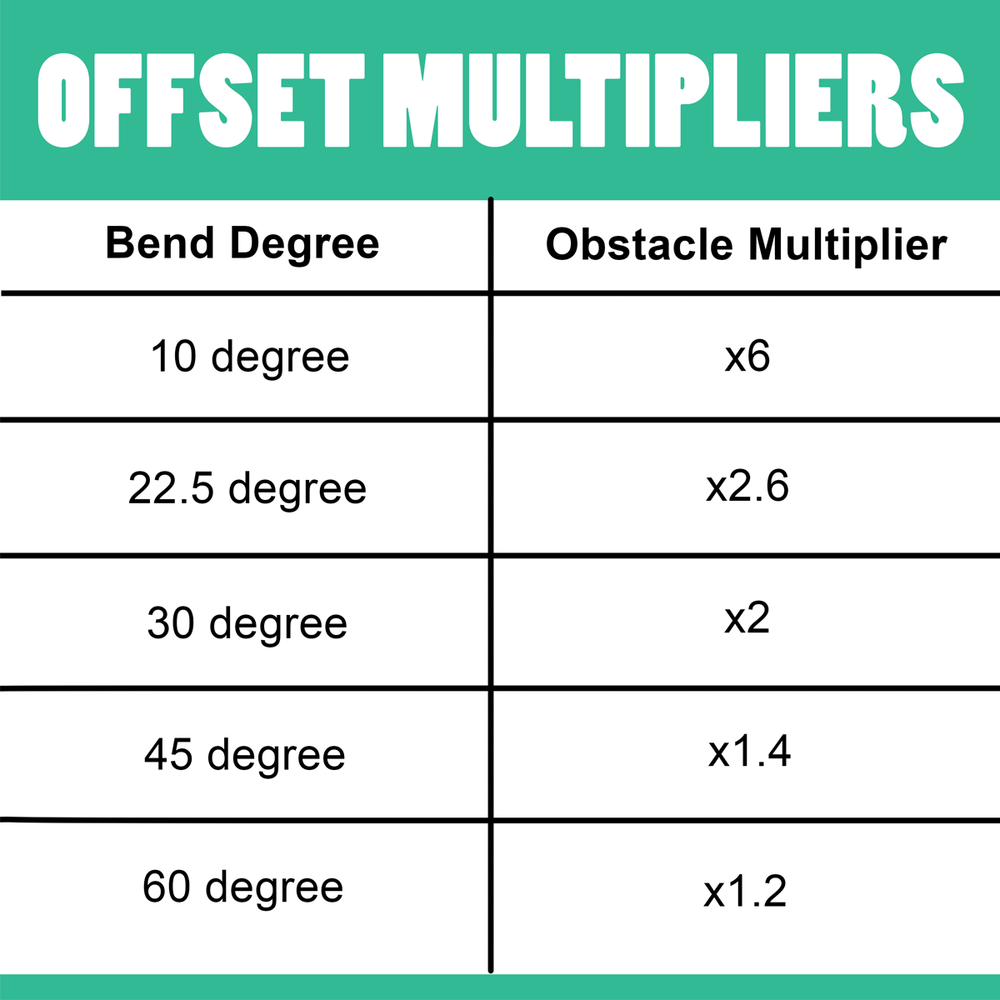
Conduit Shrinkage Chart - Web what is the conduit shrinkage—that is, the amount by which the center of the bend will be closer to the end of the conduit than the measured length of pipe? But by using a pipe and conduit bender, even the most problematic angles can be made simple; Web shrinkage is used for those that want to maximize their conduit and as long as you have the correct measurement adding for shrinkage is simple. Ed with stub, offset and outer marks. Remember to ignore the shrink when working away from the obstruction, but be sure to consider it when working into it. Web when bending two or more offsets it is necessary to advance the centers of the bends for the progressive conduits in order to maintain an equal center to center spacing. Measure length (l) from end of conduit to offset and add shrinkage (see table 3). Master bending measurements, calculations, techniques, and troubleshooting common issues with our comprehensive cheat sheet. High strength ductile iron or light weight aluminum. Web conduit bending formulas ignoring bend radius. Mark this length on conduit (c). Add the “shrink amount” from the table on page 5 to (2) bend distance, which is the horizontal length of the bend region. Figure 5 illustrates the geometry of the situation. To calculate conduit shrinkage, multiply the offset distance by the shrink per inch value. Klein tools has provided the correct stub height on each bender head. Measure length (l) from end of conduit to offset and add shrinkage (see table 3). How do you calculate conduit shrinkage? Your ideal bender has engineered features which include: But by using a pipe and conduit bender, even the most problematic angles can be made simple; Figure 5 illustrates the geometry of the situation. If bending at 10 degrees, the conduit will shrink 1/16 for every inch of rise. Locates the center of a saddle bend. How do you calculate conduit shrinkage? To find the shrink you must know the angle of the kick and put the center of that bend at the correct spot off. Web learn the basics of conduit bending, types of conduits, tools required, and safety precautions. Web conduit shrinkage refers to the shortening that occurs when a conduit is bent or offset. Your ideal bender has engineered features which include: Web these shrinkage multiplier values can be calculated using the calculator below by setting the radius to 0 and adjusting the. Web you must also consider that the conduit shrinks due to the detour. Web these shrinkage multiplier values can be calculated using the calculator below by setting the radius to 0 and adjusting the angle. High strength ductile iron or light weight aluminum. Measure the distance from the last coupling to the obstruction. I personally use it when i am. Web when bending two or more offsets it is necessary to advance the centers of the bends for the progressive conduits in order to maintain an equal center to center spacing. Conduit is inserted into the bender's head and, following the specialized guides, the user will step on the foot pedal or use their hands to bend the metal pipe. For instance for shrink, divide the bend angle by 7 and round your answer. The code further specifies that the total of all bends in a conduit run must not exceed 360°. Add the “shrink amount”from the table on For offsets, saddles and those special situations. Web what is the conduit shrinkage—that is, the amount by which the center of. Web multiplier per angle of bend (see table 2) to determine distance between bends. We know that a = 4 and angle d = 22.5º. On the conduit, measure from the free end to be bent up the calculated number and mark the conduit. Keep in mind, when bending offsets, the conduit will shrink. High strength ductile iron or light. Web when bending two or more offsets it is necessary to advance the centers of the bends for the progressive conduits in order to maintain an equal center to center spacing. Add the “shrink amount”from the table on Remember to ignore the shrink when working away from the obstruction, but be sure to consider it when working into it. There. For instance for shrink, divide the bend angle by 7 and round your answer. For offsets, saddles and those special situations. Measure length (l) from end of conduit to offset and add shrinkage (see table 3). Web multiplier per angle of bend (see table 2) to determine distance between bends. 15 degrees is 1/8 for every inch, 22.5 is 3/16,. Web when bending two or more offsets it is necessary to advance the centers of the bends for the progressive conduits in order to maintain an equal center to center spacing. (1) shrinkage, which is the reduction in horizontal length caused by the bend; Why is it essential to calculate conduit shrinkage? Frequently asked questions (faqs) q: Using the offset. Add the “shrink amount” from the table on page 5 to For offsets, saddles and those special situations. There are two formulas that i need to generate: We know that a = 4 and angle d = 22.5º. Web shrinkage is used for those that want to maximize their conduit and as long as you have the correct measurement adding. Using the offset height (z) times angle multiplier (chart below) subtract this amount from the. Remember to ignore the shrink when working away from the obstruction, but be sure to consider it when working into it. The national electric code (nec) specifies a minimum radius for conduit bends in order to avoid damage to both the conduit and conductors. I personally use it when i am not in a rush and. This calculation is crucial for ensuring the accuracy of conduit installations. Web what is the conduit shrinkage—that is, the amount by which the center of the bend will be closer to the end of the conduit than the measured length of pipe? Klein tools has provided the correct stub height on each bender head. Web shrinkage is used for those that want to maximize their conduit and as long as you have the correct measurement adding for shrinkage is simple. Web when bending two or more offsets it is necessary to advance the centers of the bends for the progressive conduits in order to maintain an equal center to center spacing. But by using a pipe and conduit bender, even the most problematic angles can be made simple; Remember to ignore the shrink when working away from the obstruction, but be sure to consider it when working into it. A change in height does not effect the calculated shrink multiplier while the radius is set to zero. Why is it essential to calculate conduit shrinkage? This document will walk a beginning electrician through the steps to bend emt tubing with a hand emt tubing bender. Plus you eliminate the need for costly conduit elbows when you make your own bends. Shrinkage (%)= (100−98 / 100)×100=2% this means the conduit has experienced a 2% shrinkage in length due to the change in temperature.Electrical Conduit Math Math Encounters Blog
Emt Conduit Bending Chart
Emt Pipe Bending Chart
3/4 Emt Shrinkage Chart
Emt Conduit Bending Chart
How To Bend Conduit change comin
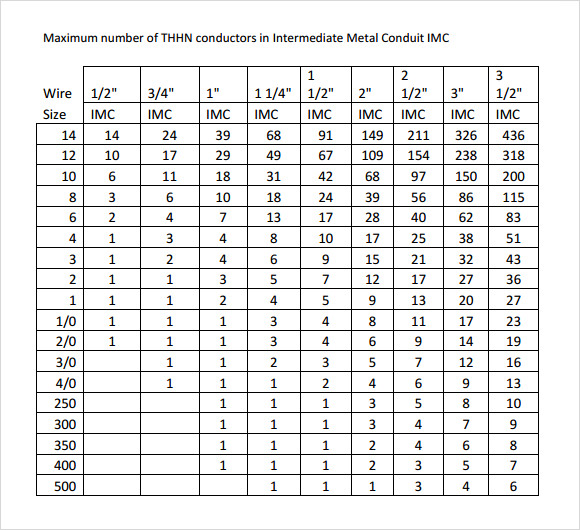
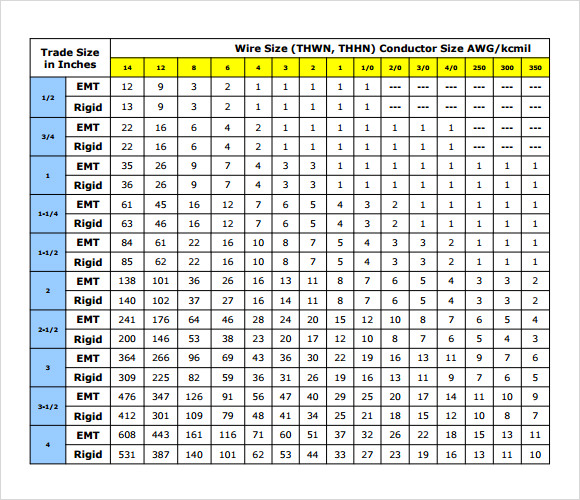
FREE 9+ Sample Conduit Fill Chart Templates in PDF
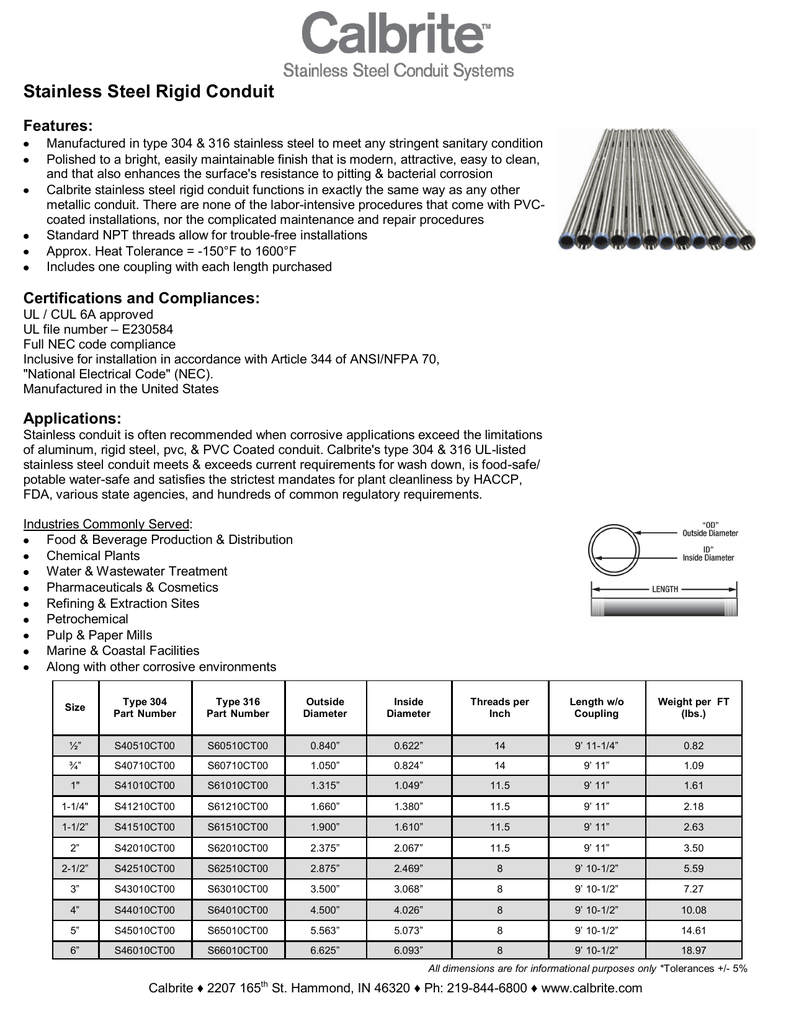
Rigid Conduit Dimension Chart
FREE 9+ Sample Conduit Fill Chart Templates in PDF
Electrical Conduit Math Math Encounters Blog
Web Learn The Basics Of Conduit Bending, Types Of Conduits, Tools Required, And Safety Precautions.
The First Bend Should Be Made At (C), Put (Star) Or B At (C).
Web These Shrinkage Multiplier Values Can Be Calculated Using The Calculator Below By Setting The Radius To 0 And Adjusting The Angle.
If Bending At 10 Degrees, The Conduit Will Shrink 1/16 For Every Inch Of Rise.
Related Post:

.png)