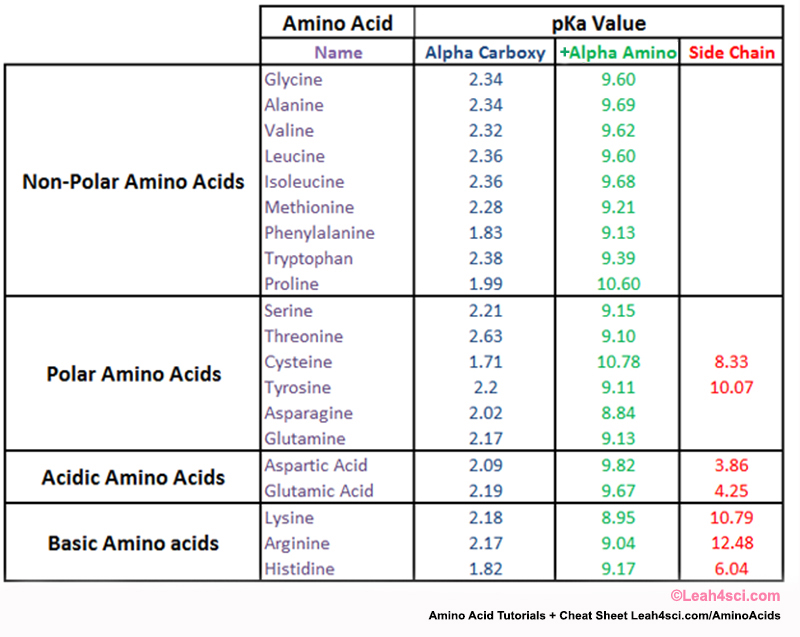
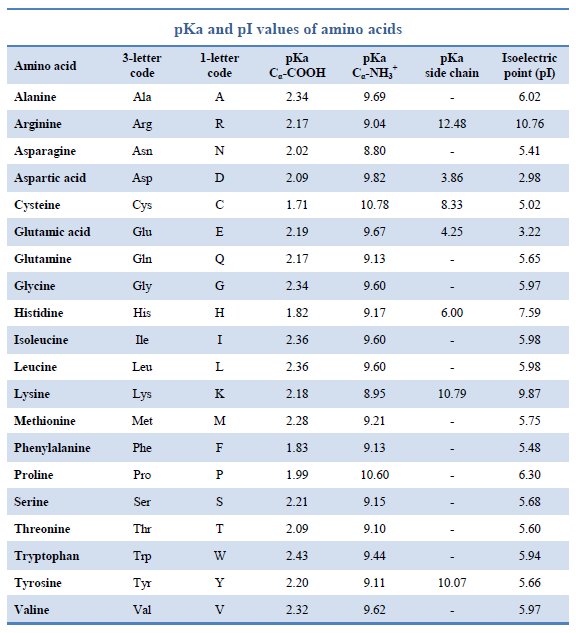
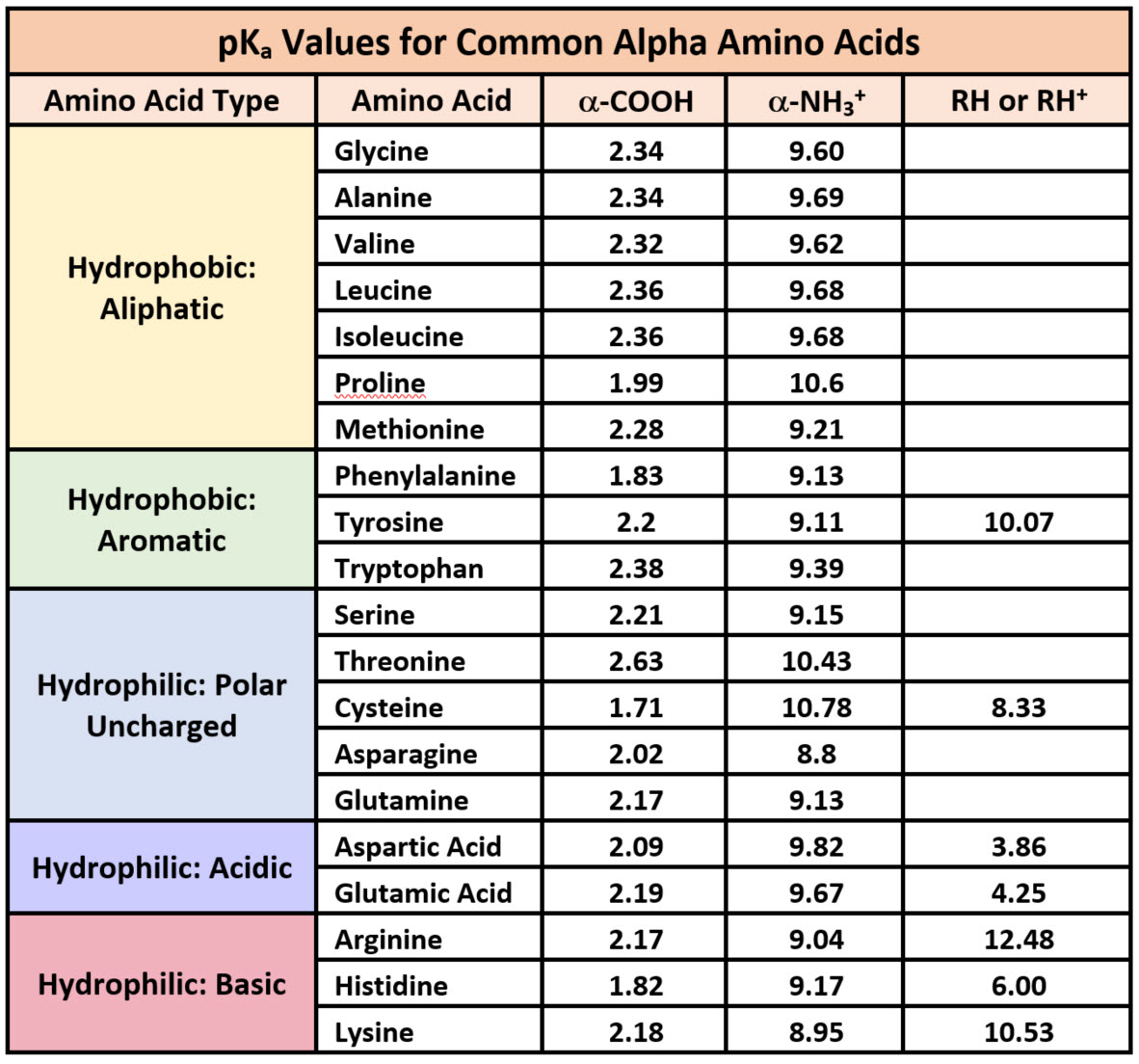
Amino Acid Pka Chart
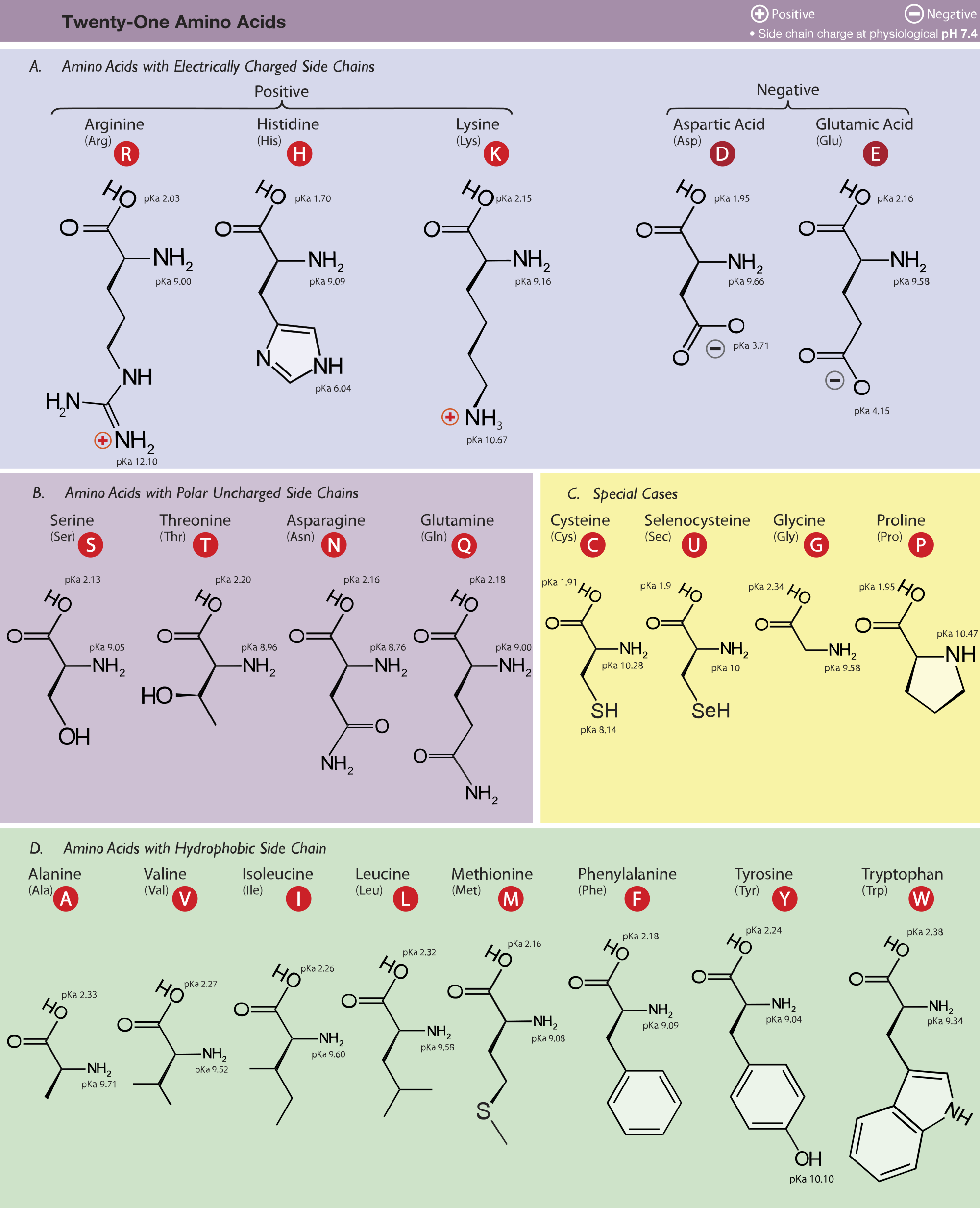
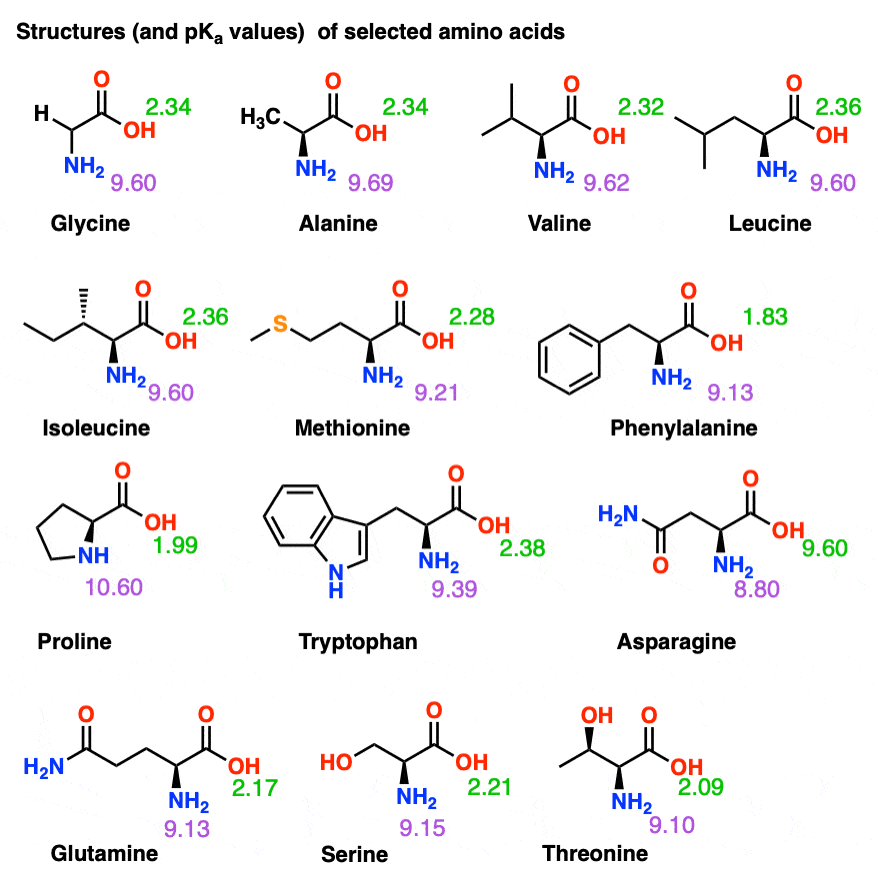
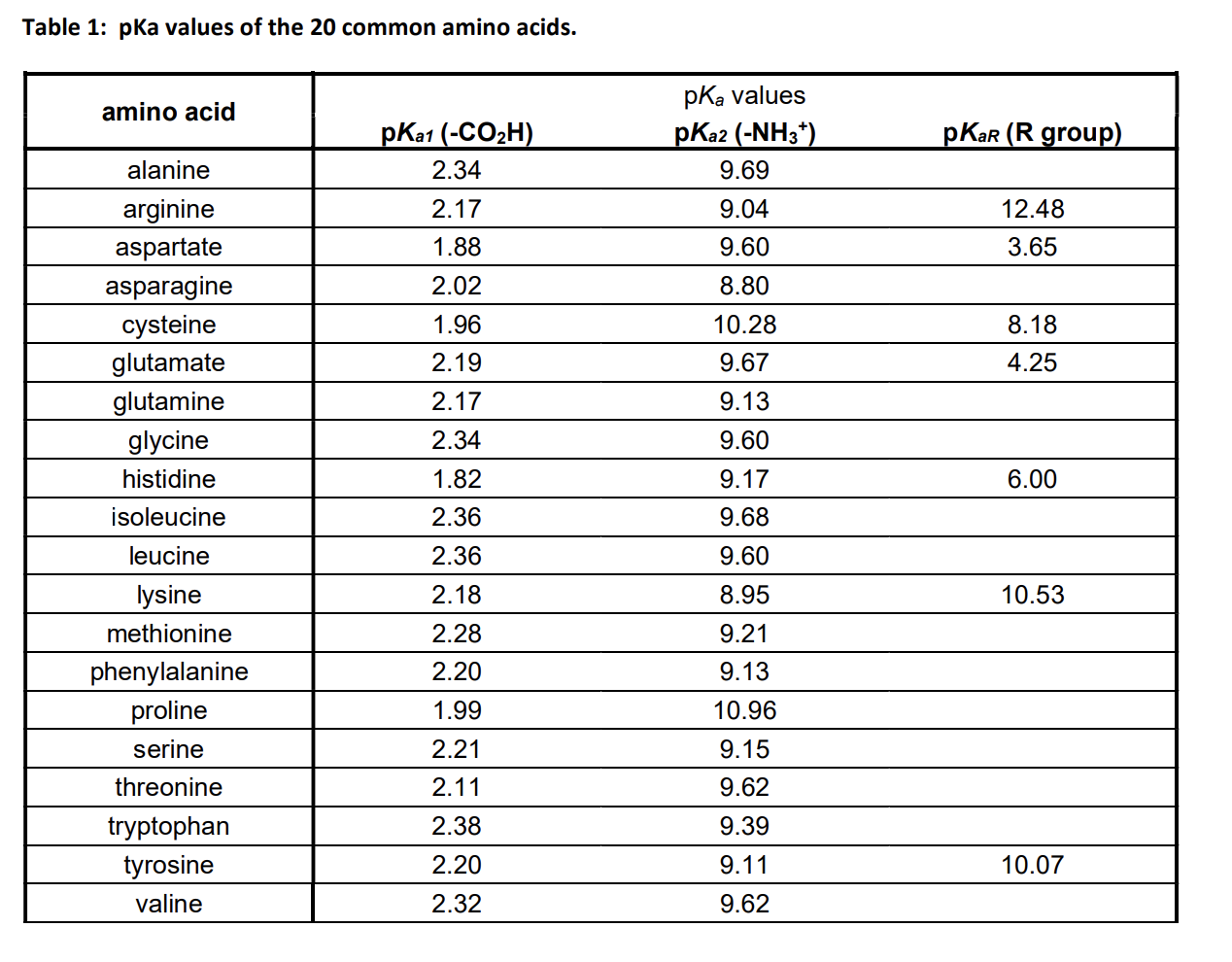
Amino Acid Pka Chart - In organic chemistry, pka is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a compound. There are 22 amino acids that are found in proteins and of these, only 20 are specified by the universal genetic code. If a molecule is a base or an acid, depends on their functional groups. Web table \(\pageindex{2}\) shows the standard pk a values for the amino acids and can be used to predict the ionization/charge status of amino acids and their resulting. The ammonium holds the proton more tightly than does the acid. Web the pka is a measure of the strength of an acid, i.e., the lower the pk a stronger the acid. Web the r group for each of the amino acids will differ in structure, electrical charge, and polarity. Web basic molecules gain protons and acidic molecules donate protons. The proton stays on the nitrogen. It represents the negative logarithm of the acid. The isoelectric point, pi, is the ph at which negative and positive charges are balanced. Web the isoelectric point of an amino acid is the ph at which the amino acid has a neutral charge. Web only the guanidine group (hnc (nh2)2) in arg (pka = 12.5) and amine group in lys (pka = 10.5) will accept a proton and exist with an overall charge of +1 at physiological ph. Web the pka of the acid is near 5, and the pka of the ammonium is near 9. The isoelectric points range from 5.5 to 6.2. At neutral ph the amino. If a molecule is a base or an acid, depends on their functional groups. Web all amino acids have the same basic structure, which is shown in figure 2.1. For the 13 amino acids with a neutral side. Web amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Web table of contents. Web table of pk a and pi values. Amino acids have −cooh − cooh group that is acidic with pk a 2. Web why are pkas so important? Web most biochemistry courses will require you to know the following: Amino acids have −cooh − cooh group that is acidic with pk a 2. Because every nucleophile is potentially a base, and vice versa. Amino acid pka and pi values Web 20 amino acids and their functions, structures, names, properties, classifications. If a molecule is a base or an acid, depends on their functional groups. Web the pka of the acid is near 5, and the pka of the ammonium is near 9. In organic chemistry, pka is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a compound. Web this is why the carboxylic acid groups of amino acids have a lower pka value of around 2, while acetic acid has a pka value of. You will learn how to calculate the isoelectric point, and the effects of ph on the. For the 13 amino acids with a neutral side. Web the isoelectric point of an amino acid is the ph at which the amino acid has a neutral charge. Web table \(\pageindex{2}\) shows the standard pk a values for the amino acids and can. Certain functional groups give away. It represents the negative logarithm of the acid. If you have a reaction where it looks like you might get sn2 or e2,. Web this is why the carboxylic acid groups of amino acids have a lower pka value of around 2, while acetic acid has a pka value of 4.76. Web only the guanidine. If you have a reaction where it looks like you might get sn2 or e2,. Amino acid pka and pi values The ammonium holds the proton more tightly than does the acid. At the “center” of each amino acid is a carbon called the α carbon and attached to it. Amino acids have −cooh − cooh group that is acidic. Web why are pkas so important? The proton stays on the nitrogen. If a molecule is a base or an acid, depends on their functional groups. Web amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Web only the guanidine group (hnc (nh2)2) in arg (pka = 12.5) and amine group in lys (pka = 10.5) will accept a proton and. Web pka and electrical properties of amino acids. If you have a reaction where it looks like you might get sn2 or e2,. Web table of pk a and pi values. Web why are pkas so important? Refer to the charts and structures below to explore amino acid properties,. Web the pka is a measure of the strength of an acid, i.e., the lower the pk a stronger the acid. The isoelectric point, pi, is the ph at which negative and positive charges are balanced. Web table of pk a and pi values. Web why are pkas so important? Web pka and electrical properties of amino acids. If a molecule is a base or an acid, depends on their functional groups. The ammonium holds the proton more tightly than does the acid. Web why are pkas so important? Web table of pk a and pi values. They contain an amino group, carboxylic acid group, alpha carbon, and side chain. In organic chemistry, pka is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a compound. Web only the guanidine group (hnc (nh2)2) in arg (pka = 12.5) and amine group in lys (pka = 10.5) will accept a proton and exist with an overall charge of +1 at physiological ph. Web kainoid synthases are key enzymes in the biosynthesis of kainoids. Amino acids have −cooh − cooh group that is acidic with pk a 2. Web 20 amino acids and their functions, structures, names, properties, classifications. If you have a reaction where it looks like you might get sn2 or e2,. They contain an amino group, carboxylic acid group, alpha carbon, and side chain. Web table of pk a and pi values. If a molecule is a base or an acid, depends on their functional groups. Most amino acids have a chiral carbon, which. The ammonium holds the proton more tightly than does the acid. There are 22 amino acids that are found in proteins and of these, only 20 are specified by the universal genetic code. You will learn how to calculate the isoelectric point, and the effects of ph on the. The isoelectric points range from 5.5 to 6.2. The isoelectric point, pi, is the ph at which negative and positive charges are balanced. Certain functional groups give away.[Infographic] Comprehensive pKa Chart r/chemistry
Amino Acid Study Guide Structure and Function Albert.io
Isoelectric Points of Amino Acids (and How To Calculate Them) Master
Solved Table 1 pKa values of the 20 common amino acids.
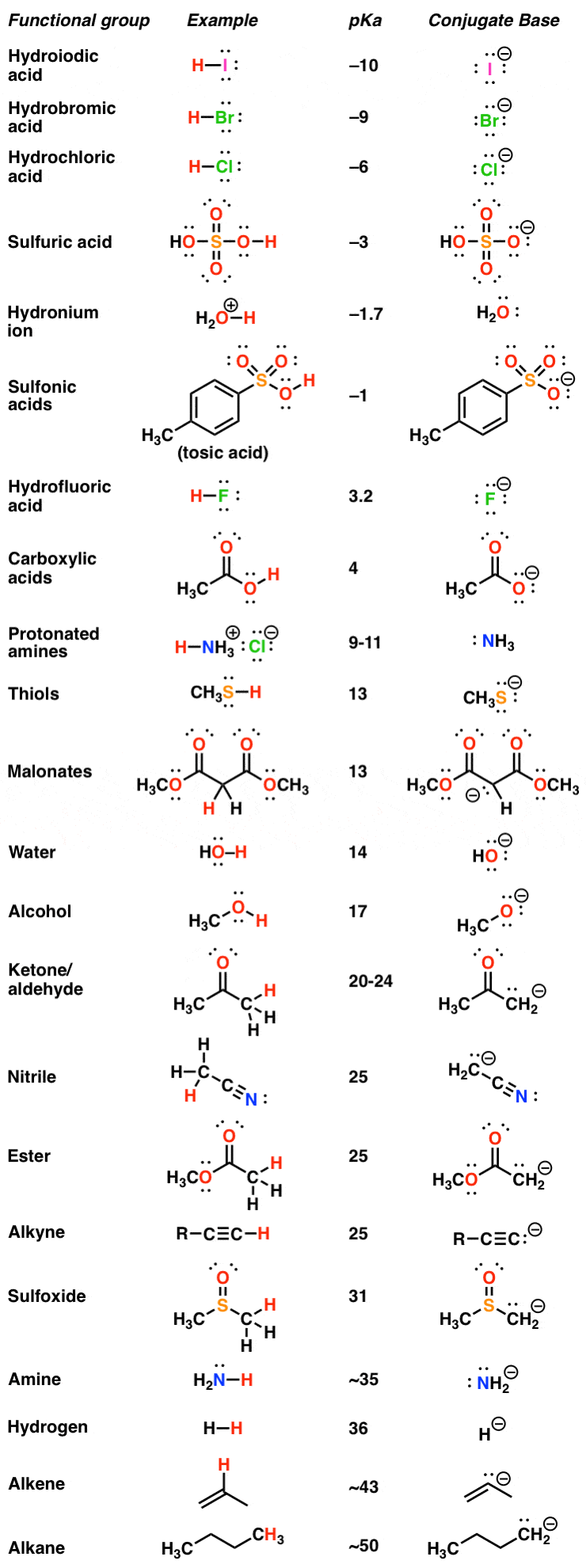
pKa Table
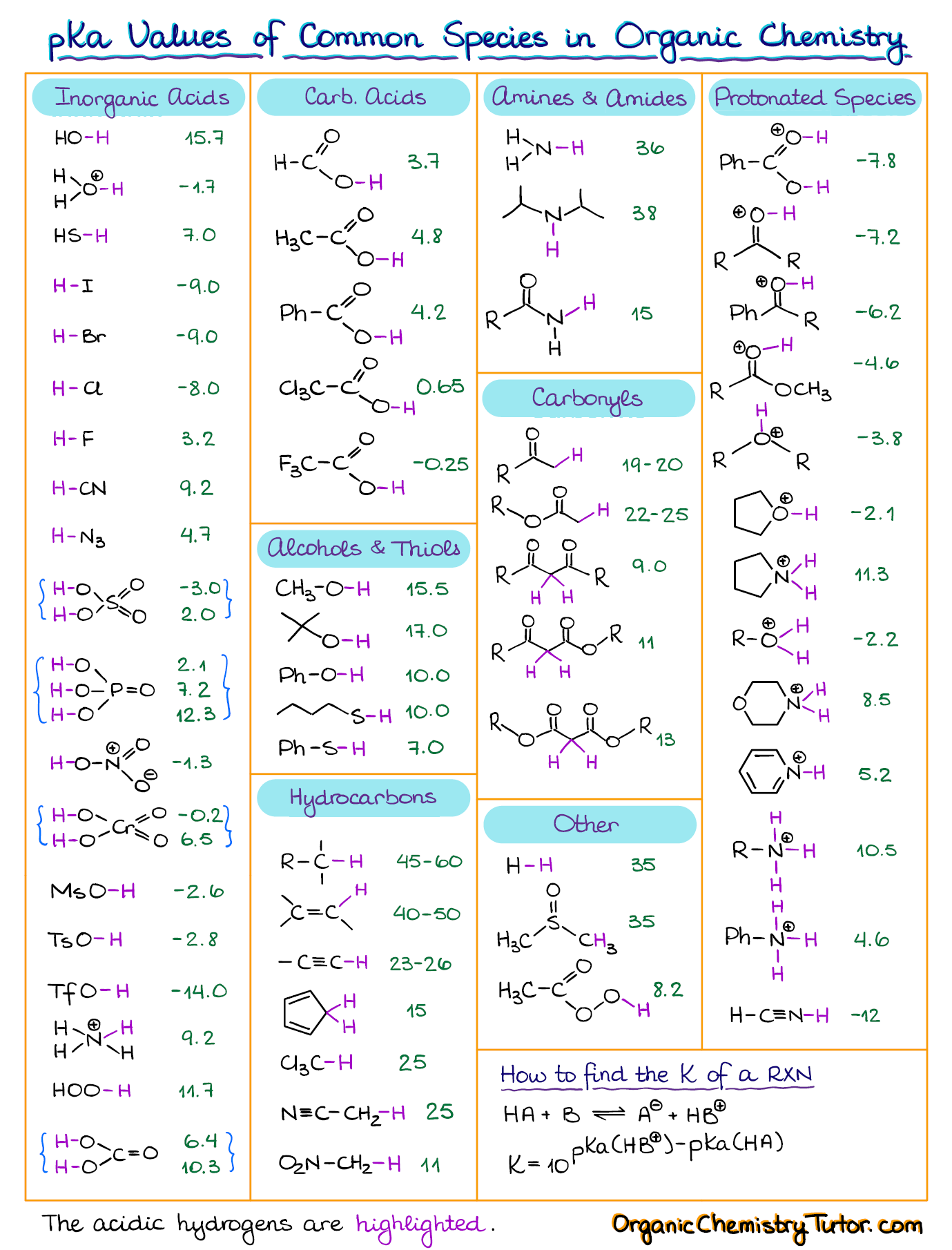
AcidBase Reactions Introducing Ka and pKa Master Organic Chemistry
Amino Acid Charge in Zwitterions and Isoelectric Point MCAT Tutorial
AcidBase Equilibrium Part 1 How to Use the pKa Table — Organic
Amino acid properties
Chapter 2 Protein Structure Chemistry
Refer To The Charts And Structures Below To Explore Amino Acid Properties,.
Because Every Nucleophile Is Potentially A Base, And Vice Versa.
Web Pka And Electrical Properties Of Amino Acids.
Web Why Are Pkas So Important?
Related Post:
![[Infographic] Comprehensive pKa Chart r/chemistry](https://external-preview.redd.it/K3Snfd3HbLKkQbUsJ8g5GMVBN8te4Altg0_bder8QLE.jpg?auto=webp&s=d6f9b865541ac9cf9c578f5146e380a014396caa)